Cumulative Update Audit
Summary
This document executes a PowerShell script to validate the full version of the OS and compares it with Microsoft's database of Windows 10/11 Cumulative Updates to identify which cumulative update the device has. The data is then formatted and stored in the Latest Cumulative Update for further auditing and monitoring purposes.
Sample Run
Dependencies
Variables
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Threshold_Days | Age of the latest installed Cumulative Update in days to determine if it is obsolete. Default is 75. |
| Output | Output of the PowerShell script gathering the data from the endpoint. |
Implementation
Create the Custom Field Latest Cumulative Update.
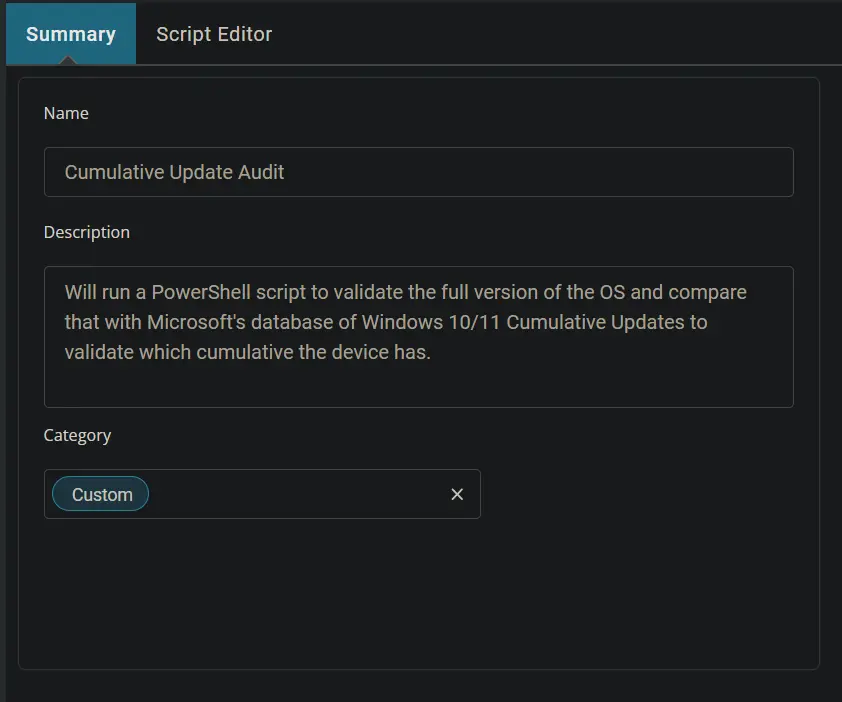
Create Script
Create a new Script Editor style script in the system to implement this Task.
Name: Cumulative Update Audit
Description: This script will run a PowerShell script to validate the full version of the OS and compare it with Microsoft's database of Windows 10/11 Cumulative Updates to identify which cumulative update the device has.
Category: Custom
Script
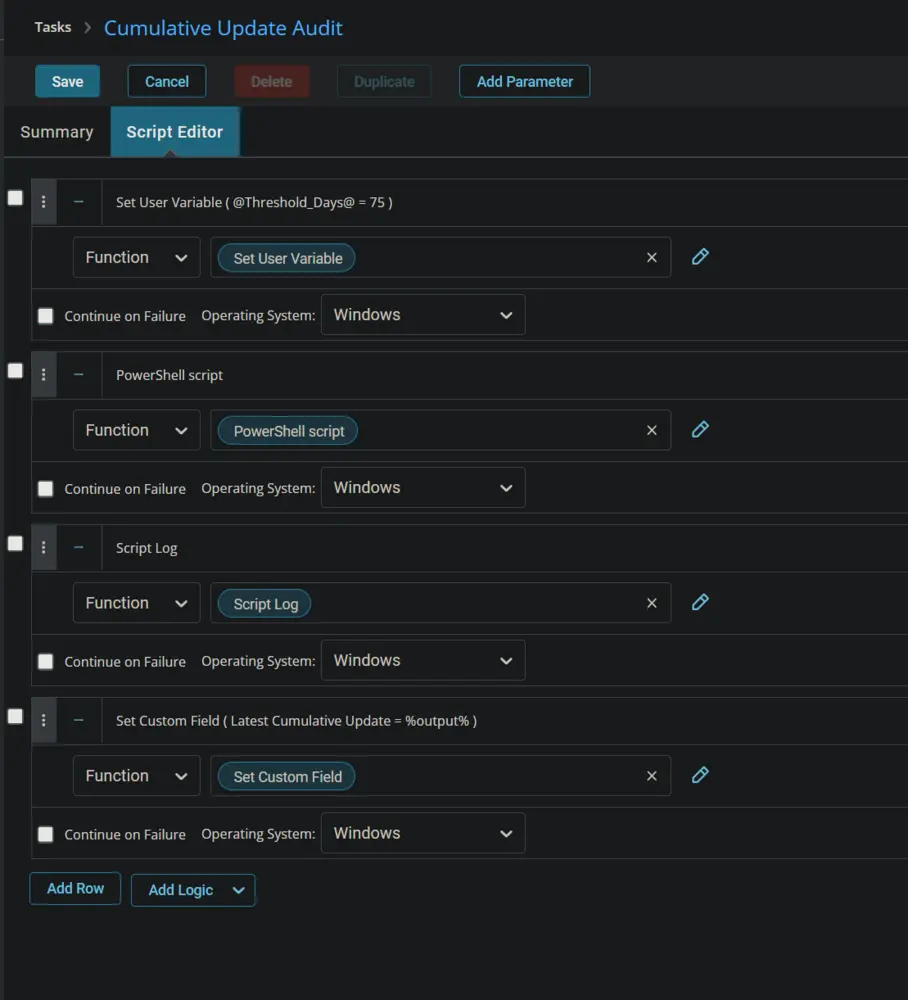
Start by adding a row. You can do this by clicking the "Add Row" button at the bottom of the script page.
Row 1 Function: Set User Variable
Type Threshold_Days for Variable Name and 75 for the value. This value represents the number of days to consider the latest installed Cumulative Update as obsolete. This threshold can be modified as needed.
The script will return Failed in the Custom Field if the most recently installed Cumulative Update on the computer is older than the days stored in this variable.
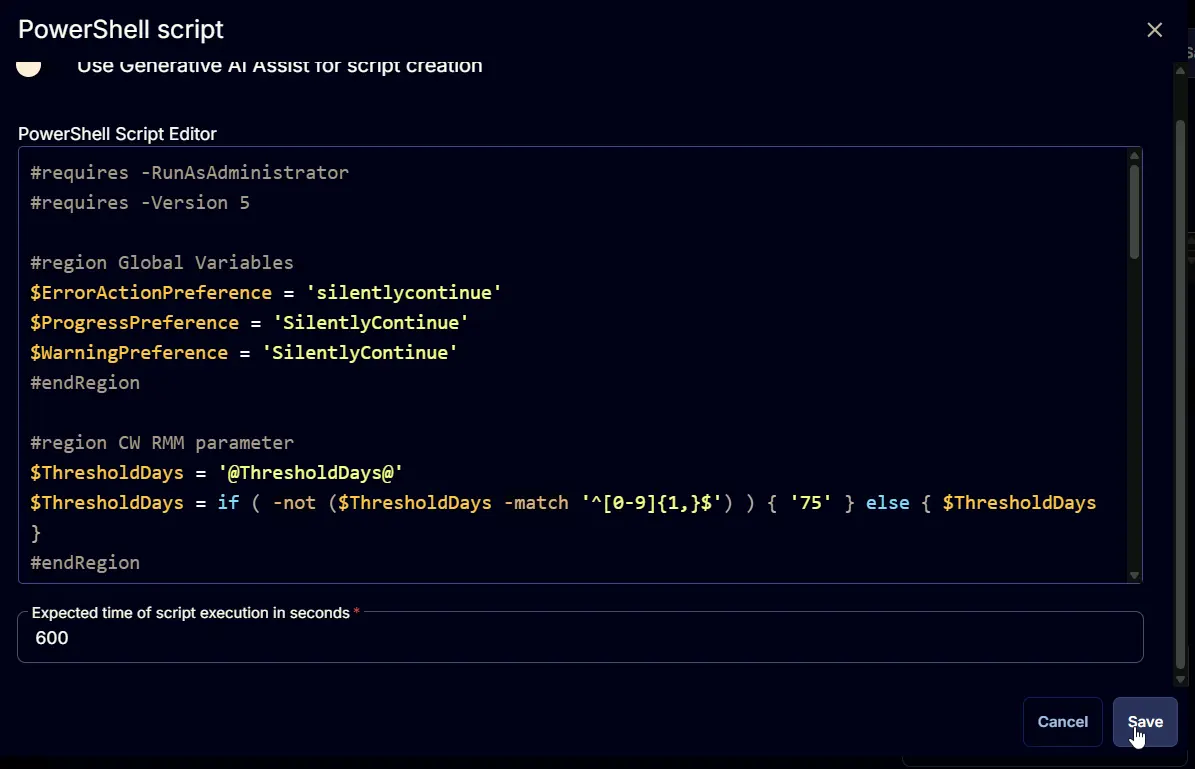
Row 2 Function: PowerShell Script
Paste in the following PowerShell script, set the expected time of script execution to 600 seconds and click the Save button.
#requires -RunAsAdministrator
#requires -Version 5
#region Global Variables
$ErrorActionPreference = 'silentlycontinue'
$ProgressPreference = 'SilentlyContinue'
$WarningPreference = 'SilentlyContinue'
#endRegion
#region CW RMM parameter
$ThresholdDays = '@ThresholdDays@'
$ThresholdDays = if ( -not ($ThresholdDays -match '^[0-9]{1,}$') ) { '75' } else { $ThresholdDays }
#endRegion
#region Setup - Variables
$ProjectName = 'Get-LatestInstalledCU'
$BaseURL = 'https://file.provaltech.com/repo'
$PS1URL = "$BaseURL/script/$ProjectName.ps1"
$WorkingDirectory = "C:\ProgramData\_automation\script\$ProjectName"
$PS1Path = "$WorkingDirectory\$ProjectName.ps1"
#endregion
#region Setup - Folder Structure
if ( !(Test-Path $WorkingDirectory ) ) {
New-Item -Path $WorkingDirectory -ItemType Directory -Force | Out-Null
}
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [enum]::ToObject([Net.SecurityProtocolType], 3072)
try {
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $PS1URL -OutFile $PS1path -UseBasicParsing -ErrorAction Stop
} catch {
if (!(Test-Path -Path $PS1Path )) {
throw ('Failed to download the script from ''{0}'', and no local copy of the script exists on the machine. Reason: {1}' -f $PS1URL, $($Error[0].Exception.Message))
}
}
#endregion
#region Execution
$CUInfo = & $ps1path
#endregion
if ( $Cuinfo -match 'Failed to gather build number|Unsupported Operating System' ) {
throw "Failure Reason: $($Cuinfo)"
} else {
$Today = Get-Date
$FormattedDate = $Today.ToString('yyyy-MM-dd')
$CompareFormat = [DateTime]$FormattedDate
$ReleaseDate = $CUInfo.ReleaseDate
$comparereleasedate = [DateTime]$ReleaseDate
$Difference = New-TimeSpan -Start $comparereleasedate -End $CompareFormat
$status = if ($Difference.Days -ge $ThresholdDays) { 'Failed' } else { 'Success' }
return "$($status). $($CUInfo.LastInstalledCU). Version: $($CUInfo.OSBuild). Date Audited: $FormattedDate"
}
Row 3 Function: Script Log
In the script log message, simply type %output% so that the script will send the results of the PowerShell script above to the output on the Automation tab for the target device.
Row 4 Function: Set Custom Field
Add a new row by clicking on the "Add Row" button.
Select Set Custom Field Function.
When you select Set Custom Field, a new window will open.
In this window, search for the Latest Cumulative Update field.
Custom Field: Latest Cumulative Update
Value: %Output%
Once all items are added, please save the task. The final task should look like the screenshot below.
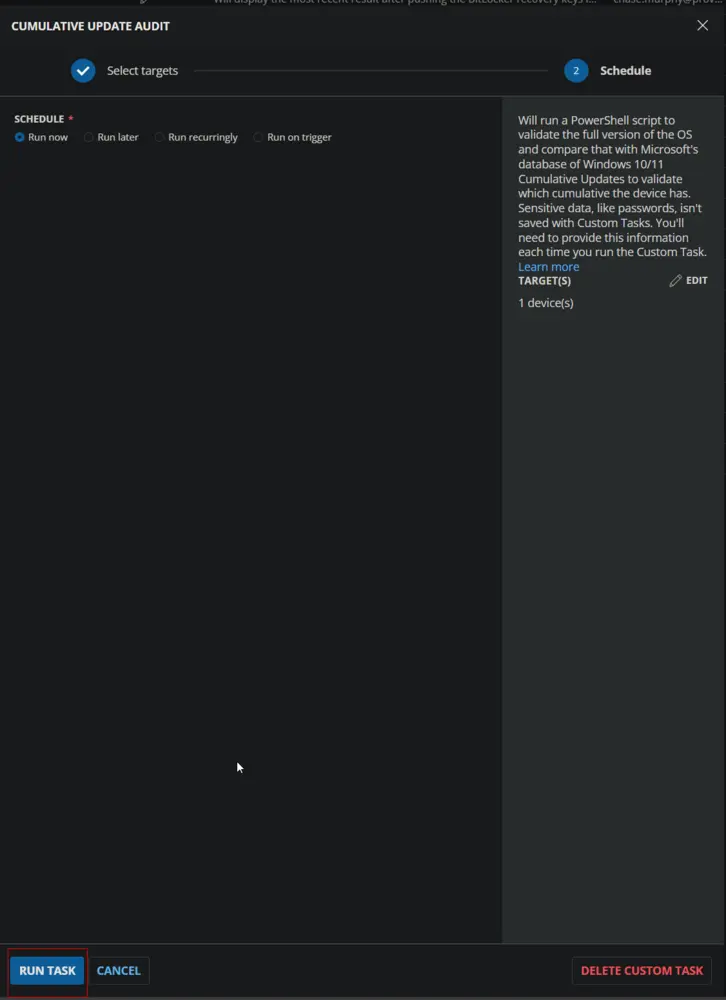
Deployment
It is suggested to run the Task once per month against Windows computers.
- Go to
Automation>Tasks. - Search for the
Cumulative Update AuditTask. - Select the concerned task.
- Click on the
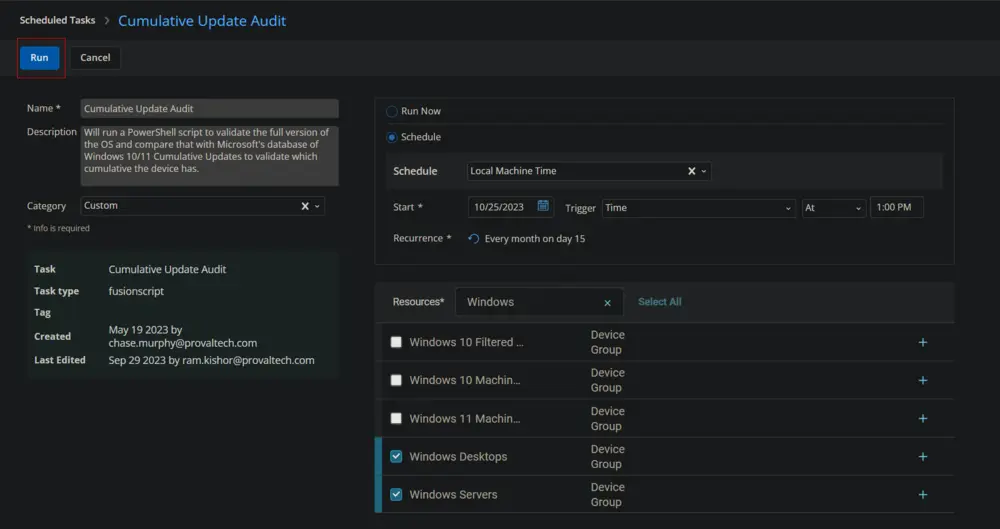
Schedulebutton to schedule the task/script.
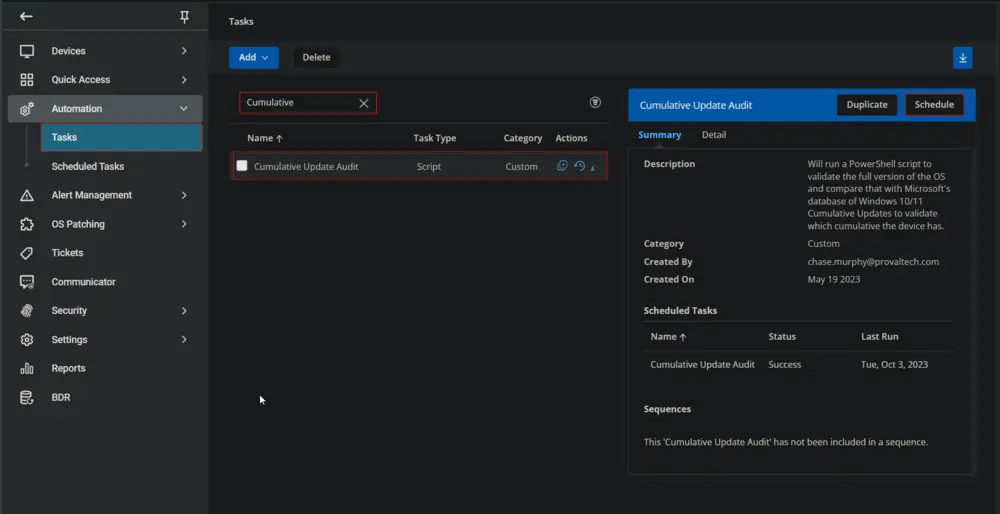
This screen will appear.
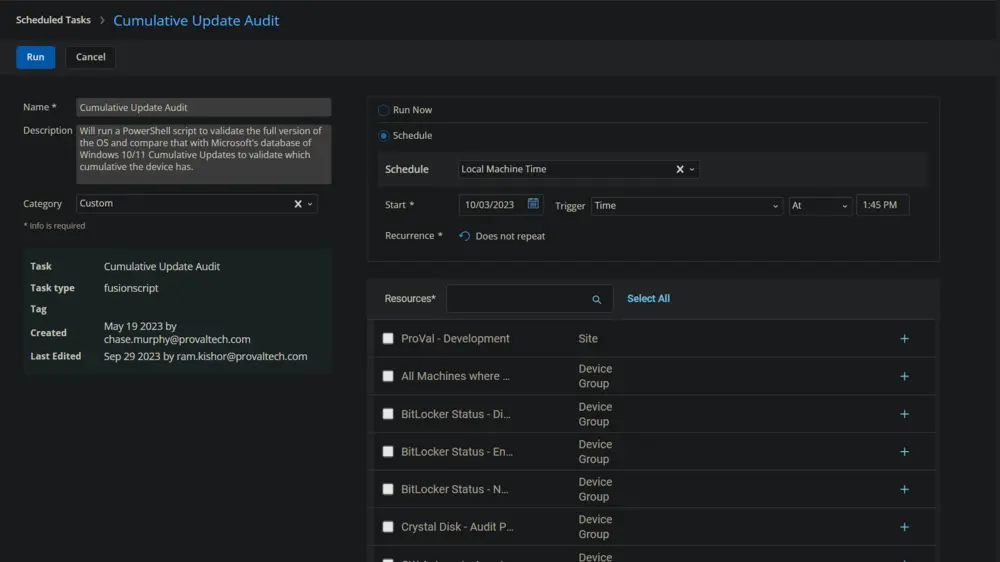
Select the relevant time to run the script and click the "Does not repeat" button.
This pop-up box will appear.
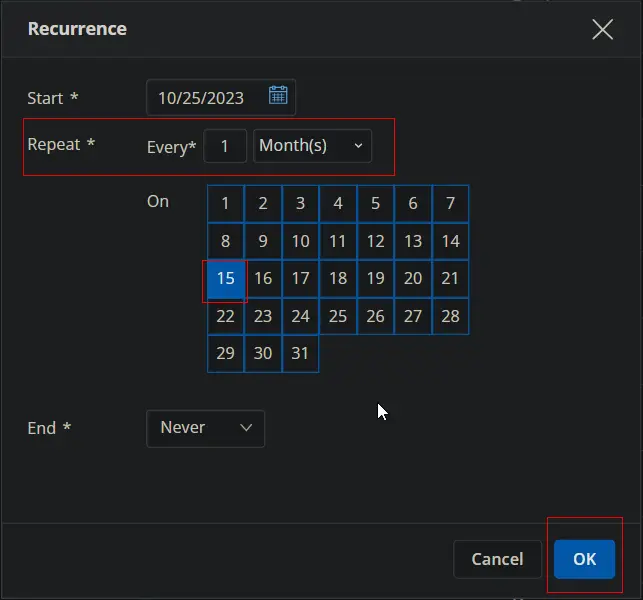
Change the Repeat interval to once per month. Here, I am selecting the 15th of every month since Microsoft releases the patches on the second Tuesday of every month.
Search for windows in the Resources* and select Windows Desktops and Windows Servers groups. You can search and select any relevant group you would like to schedule the task against.
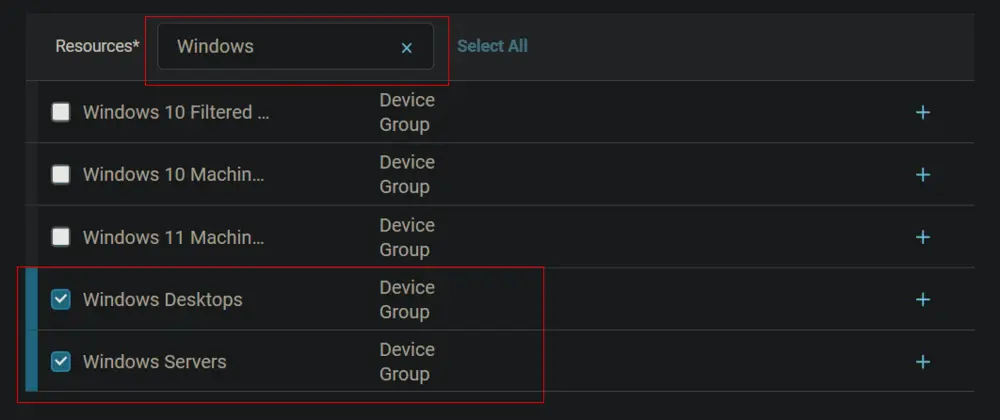
Now click the Run button to initiate the task.
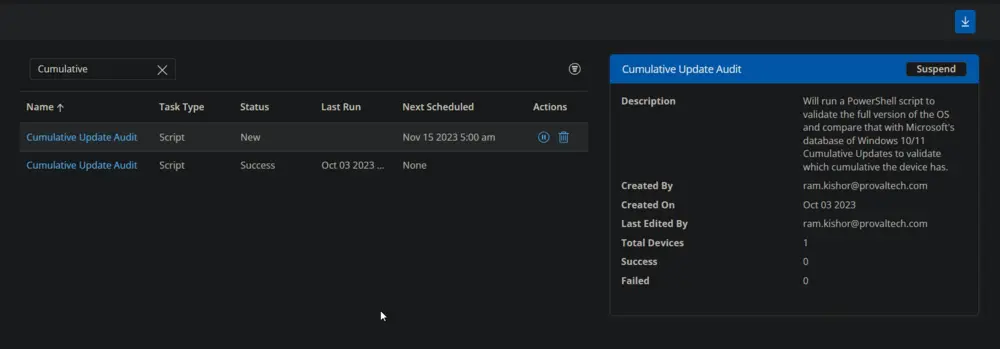
The task will start appearing in the Scheduled Tasks.
Output
-
Script log
-
Custom Field