Security - Excessive Failed Logins
Summary
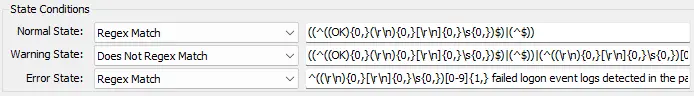
This remote monitor checks the computer for security event log event ID 4625 where the count of occurrences is greater than 10 in the last 60 minutes.
The threshold can be modified by updating the value of the $th variable in the remote monitor's command. Change this value from 10 to the desired value after importing the remote monitor.
The monitor set may not perform as expected for PowerShell versions older than 5.
Details
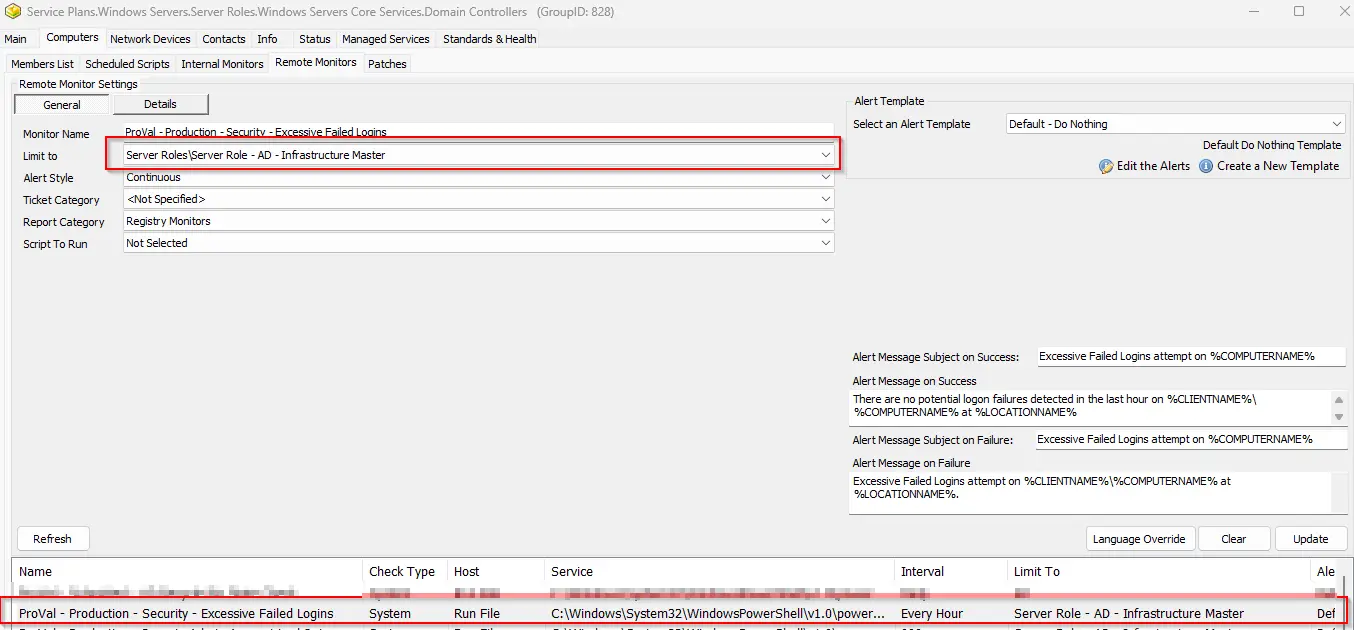
Suggested "Limit to": Server Role - AD - Infrastructure Master
Suggested Alert Style: Continuous
Suggested Alert Template: △ Custom - Ticket Creation Computer - Failures Only
| Check Action | Server Address | Check Type | Execute Info | Comparator | Interval | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| System | 127.0.0.1 | Run File | REDACTED | State Based | 3600 | <Shown Below> |
Dependencies
Alert Template: Ticket Creation - Computer [Failures Only]
Target
Domain Controllers
Alerting
Subject: Excessive Failed Logins attempt on %COMPUTERNAME%
Alert Message on Success: There are no potential logon failures detected in the last hour on %CLIENTNAME%\%COMPUTERNAME% at %LOCATIONNAME%
Alert Message on Failure:
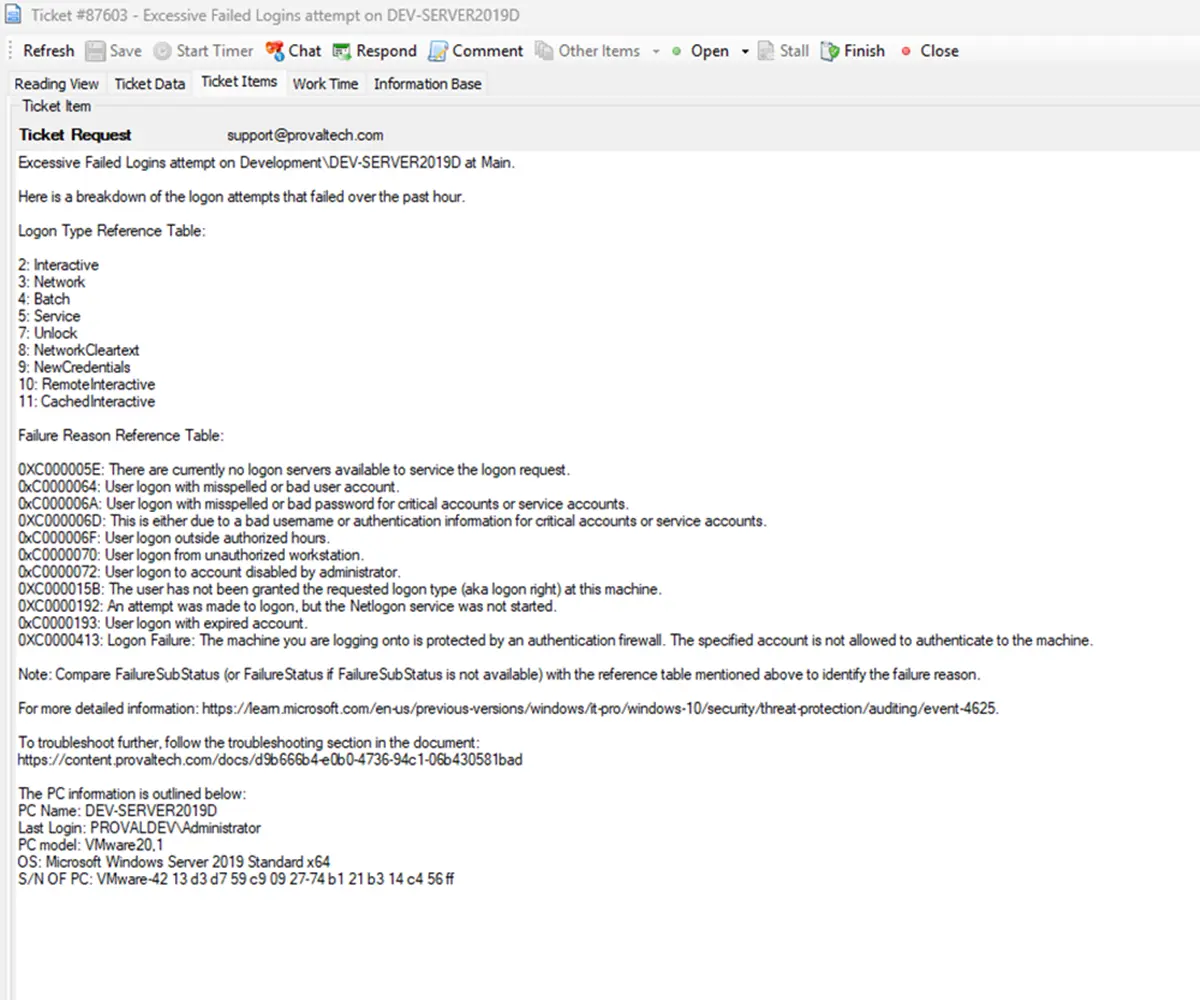
Excessive Failed Logins attempt on %CLIENTNAME%%COMPUTERNAME% at %LOCATIONNAME%.
Here is a breakdown of the logon attempts that failed over the past hour.
%RESULT%
Logon Type Reference Table:
2: Interactive
3: Network
4: Batch
5: Service
7: Unlock
8: NetworkCleartext
9: NewCredentials
10: RemoteInteractive
11: CachedInteractive
Failure Reason Reference Table:
0XC000005E: There are currently no logon servers available to service the logon request.
0xC0000064: User logon with misspelled or bad user account.
0xC000006A: User logon with misspelled or bad password for critical accounts or service accounts.
0XC000006D: This is either due to a bad username or authentication information for critical accounts or service accounts.
0xC000006F: User logon outside authorized hours.
0xC0000070: User logon from unauthorized workstation.
0xC0000072: User logon to account disabled by administrator.
0XC000015B: The user has not been granted the requested logon type (aka logon right) at this machine.
0XC0000192: An attempt was made to logon, but the Netlogon service was not started.
0xC0000193: User logon with expired account.
0XC0000413: Logon Failure: The machine you are logging onto is protected by an authentication firewall. The specified account is not allowed to authenticate to the machine.
Note: Compare FailureSubStatus (or FailureStatus if FailureSubStatus is not available) with the reference table mentioned above to identify the failure reason.
For more detailed information: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/windows/it-pro/windows-10/security/threat-protection/auditing/event-4625
To troubleshoot further, follow the troubleshooting section in the document: https://content.provaltech.com/docs/d9b666b4-e0b0-4736-94c1-06b430581bad
Sample Ticket:
Implementation
Import - Possible Brute Force Attack
Troubleshooting
General Troubleshooting Steps:
1. Identify the Account Type:
-
Domain Account:Check in Active Directory Users and Computers (ADUC). -
Local Account:Use Computer Management > Local Users and Groups. -
Service Account:Check services or scheduled tasks using the account. -
Unknown Account:Investigate for potential brute-force or enumeration attacks.
2. Review Event Logs:
- Look for Event ID
4625in the Security log.
3. Pay attention to:
-
Status/SubStatus codes
-
Logon Type
-
Source IP/Workstation
-
Target Account Name
4. Error Code Specific Troubleshooting:
| Error Code | Meaning | Action Steps |
|---|---|---|
| 0xC000006A | Bad password |
|
| 0xC000006D | Bad username or auth info |
|
| 0xC0000064 | Bad or misspelled username |
|
| 0xC000005E | No logon servers available |
|
| 0xC000006F | Logon outside authorized hours |
|
| 0xC0000070 | Unauthorized workstation |
|
| 0xC0000072 | Account disabled |
|
| 0xC000015B | Logon type not granted |
|
| 0xC0000192 | Netlogon service not started |
|
| 0xC0000193 | Expired account |
|
| 0xC0000413 | Auth firewall restriction |
|
5. Service Account Specific Checks:
-
Find Services Using the Account.
-
Run:
Get-WmiObject win32_service | Where-Object { $_.StartName -like "*accountname*" }
Or check manually in Services.msc.
6. Update Password:
-
Change the password in AD.
-
Update it in all services, scheduled tasks, and applications using it.
7. If the Account is Unknown or Suspicious
Investigate Source IP:Use firewall logs or SIEM tools.Check for Patterns:Repeated failures from the same IP or targeting multiple accounts.Block IP or Account:If malicious, take immediate action.Enable Account Lockout Policies:To prevent brute-force attacks or excessive logon attempts.