Set Last Logged In User
Summary
This is an RMM implementation of the agnostic script Set-LastLoggedOnUser to manage the last logged-in user's information displayed on the Windows login screen.
Sample Run
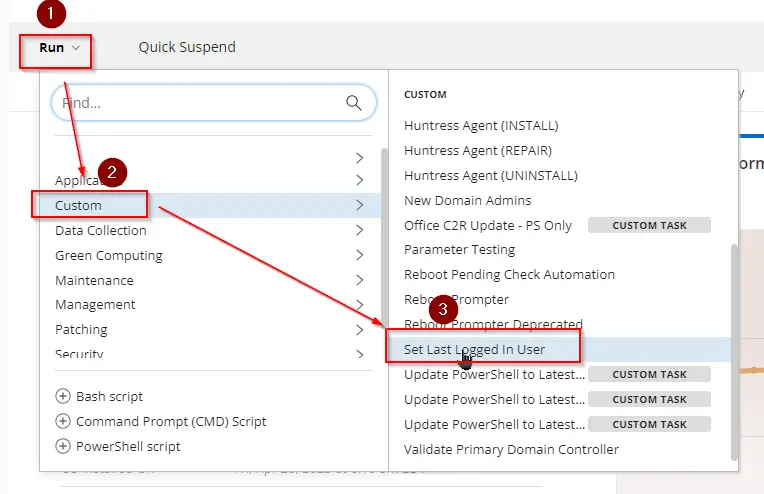
-
Select the parameters below to clear the last logged-in user's information from the login screen. The computer must be restarted manually afterward to implement the changes.
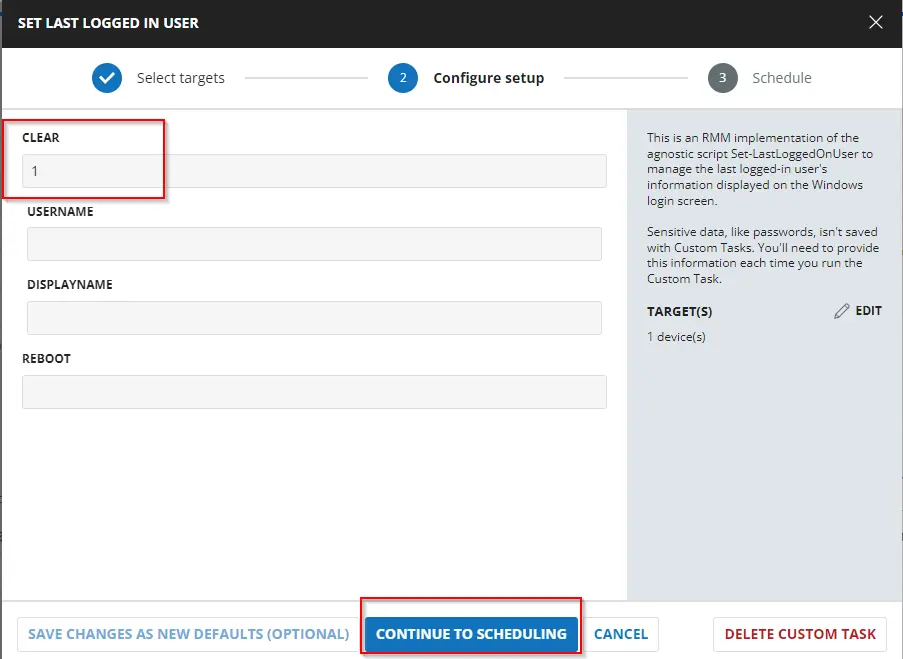
-
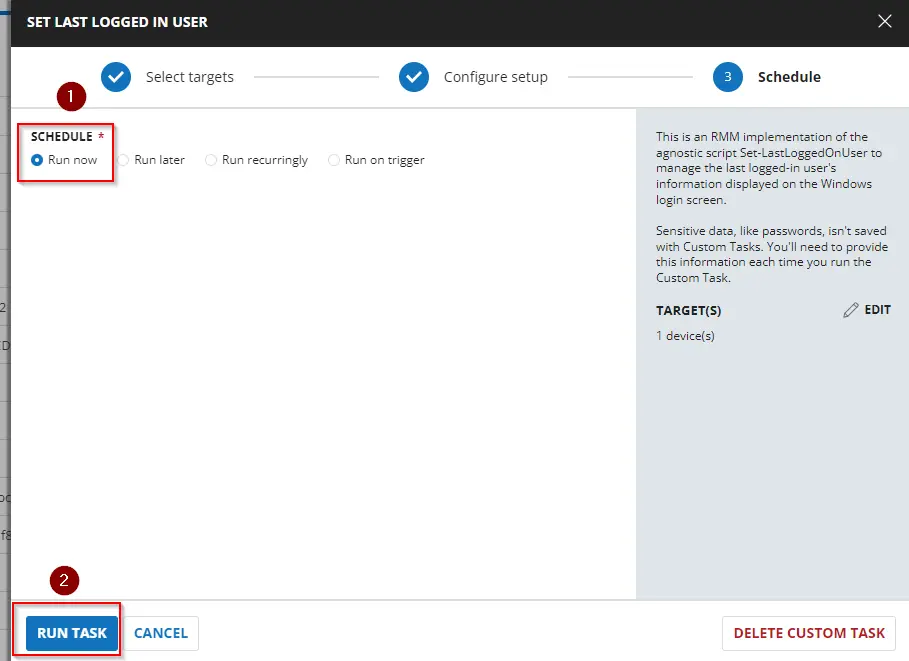
Similarly, to clear the last logged-in user's information from the login screen and forcefully restart the computer, select the parameters below.
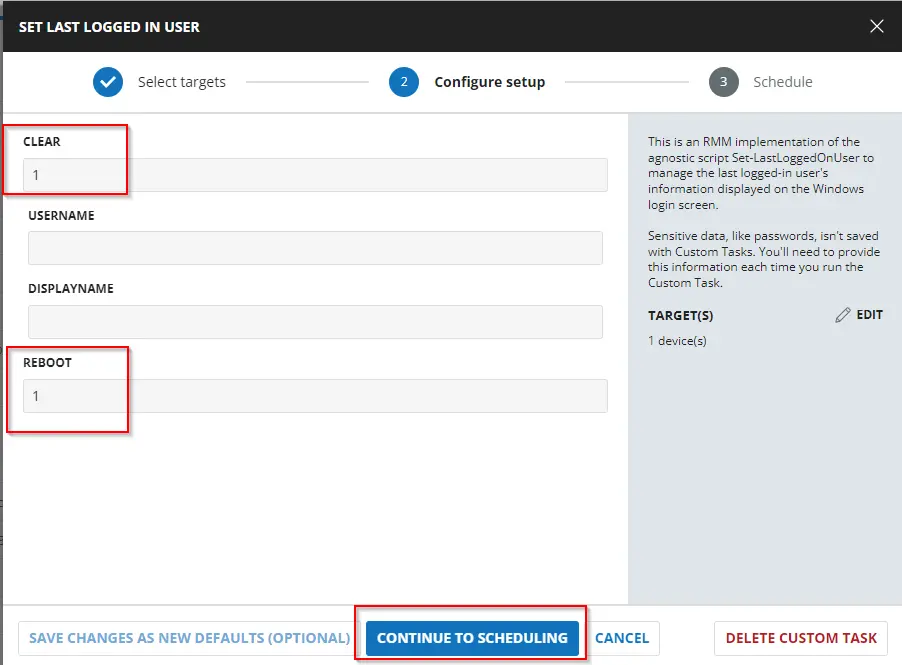
-
The parameters below set the specified local user as the last logged-in user. The computer must be restarted manually afterward to implement the changes.
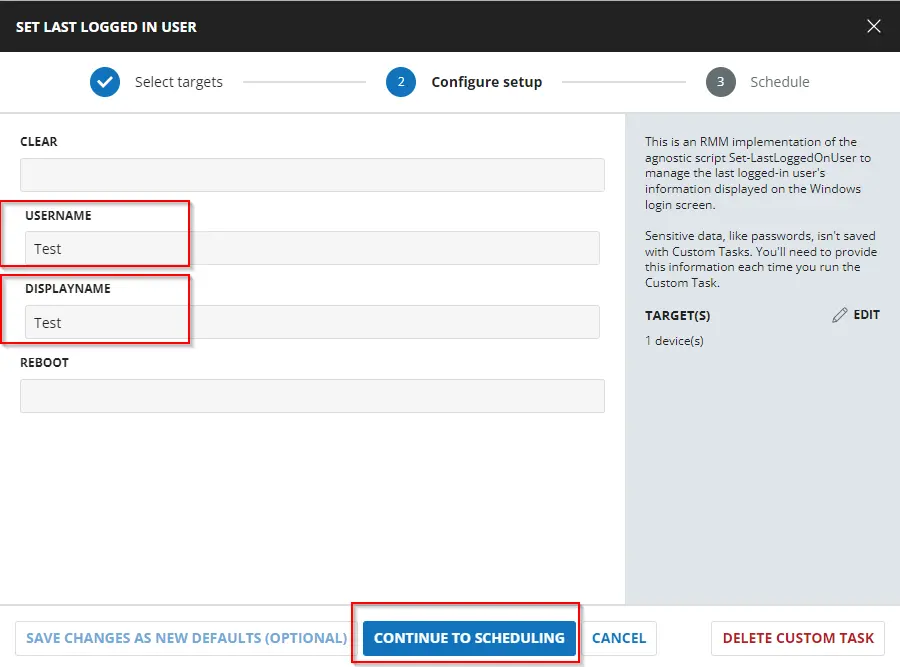
-
The parameters below set the specified domain user as the last logged-in user and forcefully restart the computer.
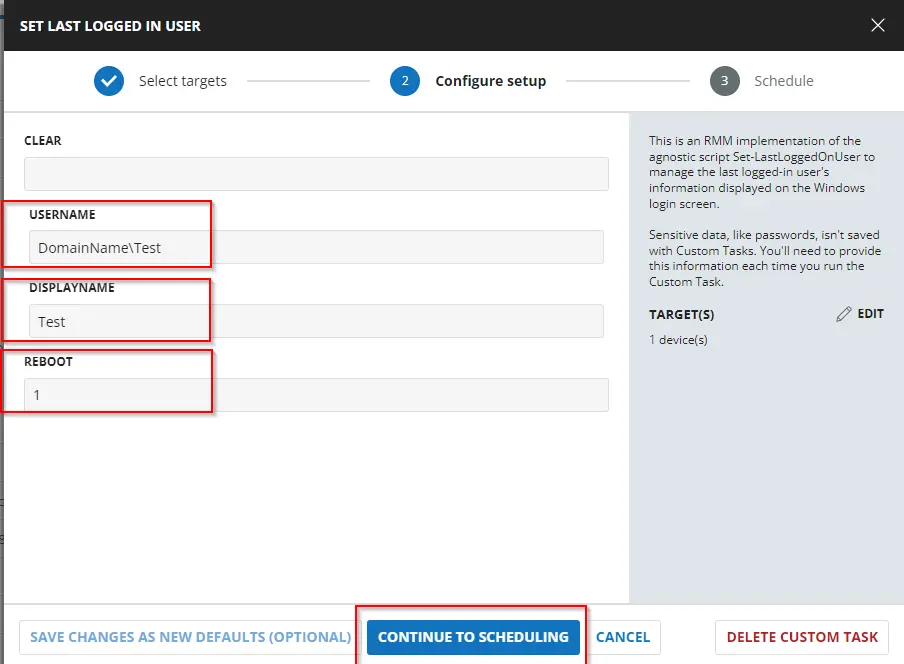
Dependencies
User Parameters
| Name | Example | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clear | 1 | True | Clears the last logged-in user's information from the login screen. |
| UserName | Domain/UserName | False | Sets the specified username as the last logged-in user. The username should be in the format 'Domain/User' or 'User'. |
| DisplayName | User Name | False | Optionally specifies the display name to set for the last logged-in user. If not provided, it defaults to the username. |
| Reboot | 1 | False | Optionally restarts the computer to apply the changes immediately. |
Task Creation
Create a new Script Editor style script in the system to implement this Task.
Name: Set Last Logged In User
Description: This script manages the last logged-in user's information displayed on the Windows login screen and can optionally restart the computer to apply changes.
Category: Custom
Parameters
Add a new parameter by clicking the Add Parameter button present at the top-right corner of the screen.
This screen will appear.
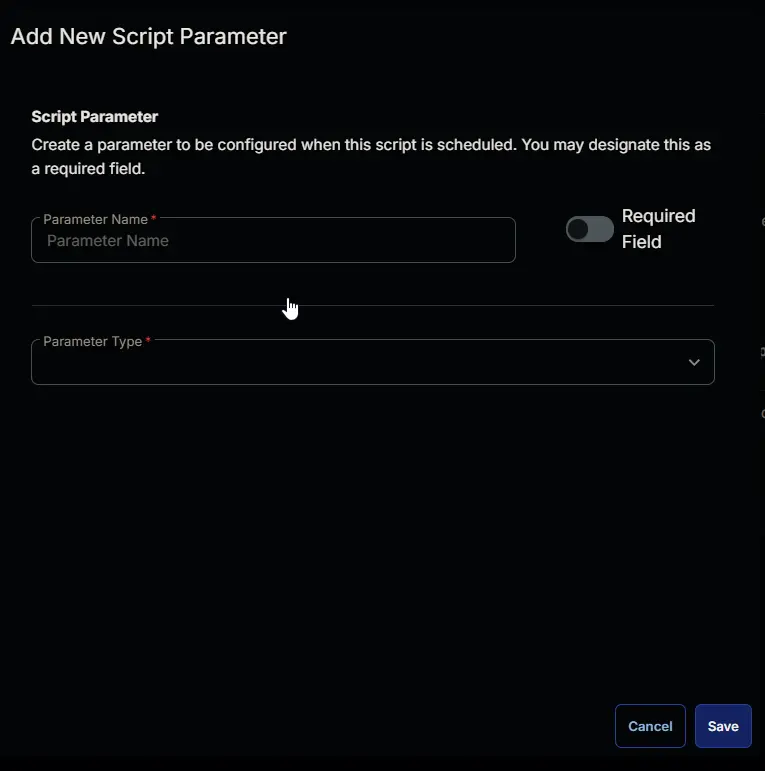
-
Set
Clearin theParameter Namefield. -
Select
Number Valuefrom theParameter Typedropdown menu. -
Click the
Savebutton.
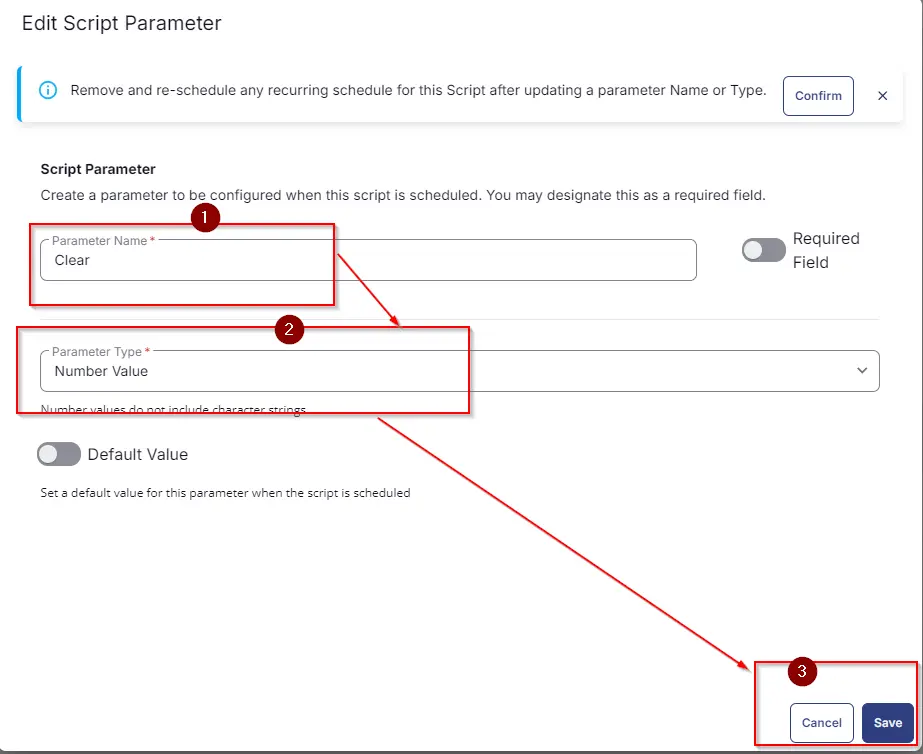
-
It will ask for confirmation to proceed. Click the
Confirmbutton to create the parameter.
Add another parameter by clicking the Add Parameter button present at the top-right corner of the screen.
-
Set
UserNamein theParameter Namefield. -
Select
Text Stringfrom theParameter Typedropdown menu. -
Click the
Savebutton.
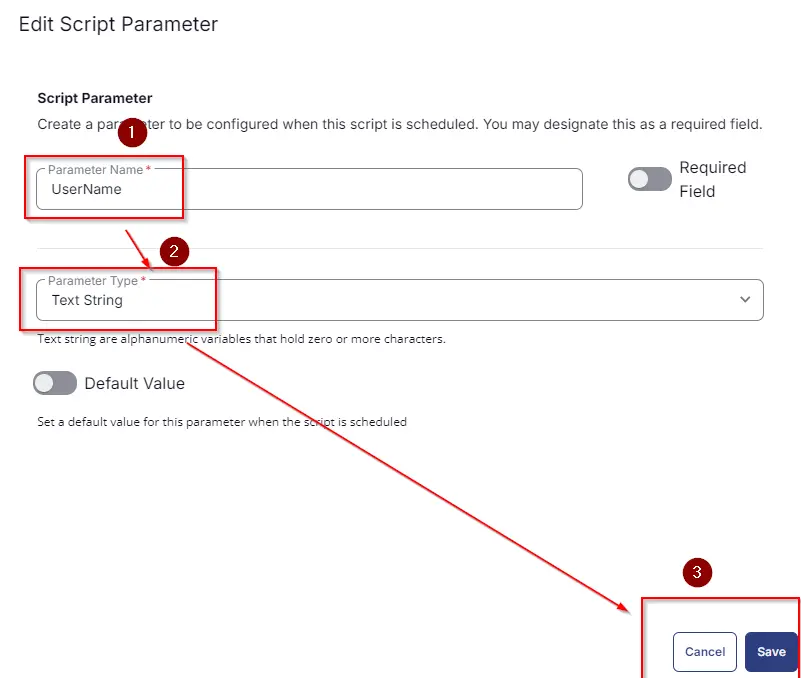
-
It will ask for confirmation to proceed. Click the
Confirmbutton to create the parameter.
Add another parameter by clicking the Add Parameter button present at the top-right corner of the screen.
- Set
DisplayNamein theParameter Namefield. - Select
Text Stringfrom theParameter Typedropdown menu. - Click the
Savebutton. - It will ask for confirmation to proceed. Click the
Confirmbutton to create the parameter.
Add another parameter by clicking the Add Parameter button present at the top-right corner of the screen.
- Set
Rebootin theParameter Namefield. - Select
Number Valuefrom theParameter Typedropdown menu. - Click the
Savebutton. - It will ask for confirmation to proceed. Click the
Confirmbutton to create the parameter.
All the parameters will look like the following:
Task
Navigate to the Script Editor Section and start by adding a row. You can do this by clicking the Add Row button at the bottom of the script page.
A blank function will appear.
Row 1 Function: PowerShell Script
Search and select the PowerShell Script function.
The following function will pop up on the screen:
Paste the following PowerShell script and set the expected time of script execution to 900 seconds. Click the Save button.
$Clear = "@Clear@"
$UserName = "@UserName@"
$DisplayName = "@DisplayName@"
$Reboot = "@Reboot@"
#region Setup - Variables
$ProjectName = 'Set-LastLoggedOnUser'
# # Parameters and Globals
# # Be sure that the name of the hashtable property matches the name of the parameter of the script that you are calling.
if ( $Clear -eq 1 ) {
$parameters = @{
Clear = $true
Restart = $Reboot -eq 1
}
} else {
$parameters = @{
UserName = $UserName
DisplayName = if ( $DisplayName -match '[0-9A-z_]' ) { $DisplayName } else { $($UserName -split '\\')[-1] }
Restart = $Reboot -eq 1
}
}
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [enum]::ToObject([Net.SecurityProtocolType], 3072)
$BaseURL = 'https://file.provaltech.com/repo'
$PS1URL = "$BaseURL/script/$ProjectName.ps1"
$WorkingDirectory = "C:\ProgramData\_automation\script\$ProjectName"
$PS1Path = "$WorkingDirectory\$ProjectName.ps1"
$Workingpath = $WorkingDirectory
$LogPath = "$WorkingDirectory\$ProjectName-log.txt"
$ErrorLogPath = "$WorkingDirectory\$ProjectName-Error.txt"
#endregion
#region Setup - Folder Structure
mkdir -Path $WorkingDirectory -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue | Out-Null
try {
Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $PS1URL -OutFile $PS1path -UseBasicParsing -ErrorAction Stop
} catch {
if (!(Test-Path -Path $PS1Path )) {
throw ('Failed to download the script from ''{0}'', and no local copy of the script exists on the machine. Reason: {1}' -f $PS1URL, $($Error[0].Exception.Message))
}
}
#endregion
#region Execution
if ($Parameters) {
& $PS1Path @Parameters
} else {
& $PS1Path
}
#endregion
if ( !(Test-Path $LogPath) ) {
Throw 'PowerShell Failure. A Security application seems to have restricted the execution of the PowerShell Script.'
}
if ( Test-Path $ErrorLogPath ) {
$ErrorContent = ( Get-Content -Path $ErrorLogPath )
throw $ErrorContent
}
Get-Content -Path $LogPath
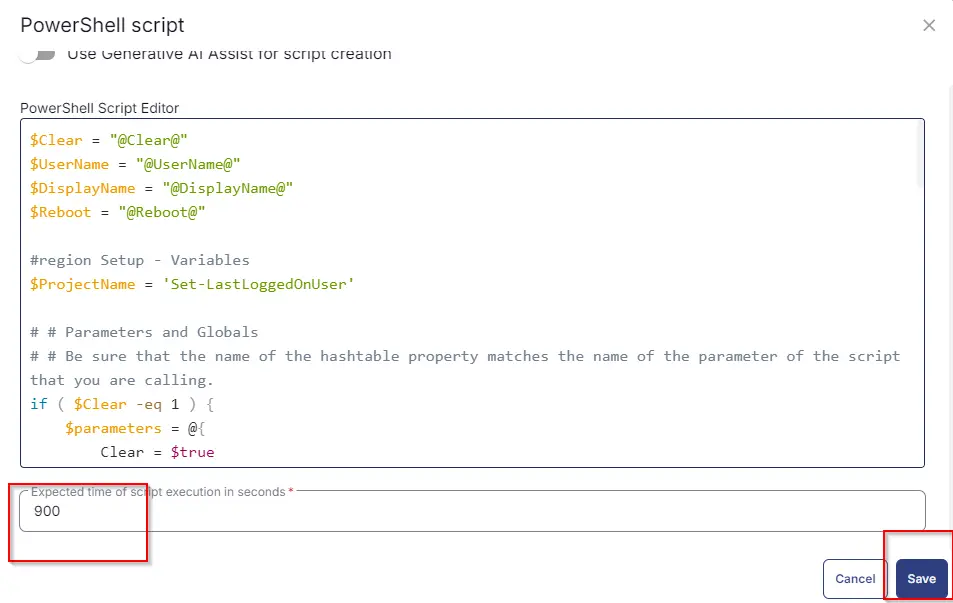
Click the Save button at the top-right corner of the screen to save the script.
Completed Task
Output
- Script Log