CU Compliance and Audit - All Machines
Summary
The CU Compliance and Audit - All Machines report provides a high-level overview of the patch health across the entire client environment, including both servers and workstations. Unlike standard patch reports that may simply count missing patches, this report focuses on the "freshness" of the operating system by calculating the age of the last installed Cumulative Update (CU).
This approach helps identify machines that might report as "Fully Patched" in RMM but are actually stuck on an older monthly update due to failing Windows Update agents or other errors.
Compliance Calculation
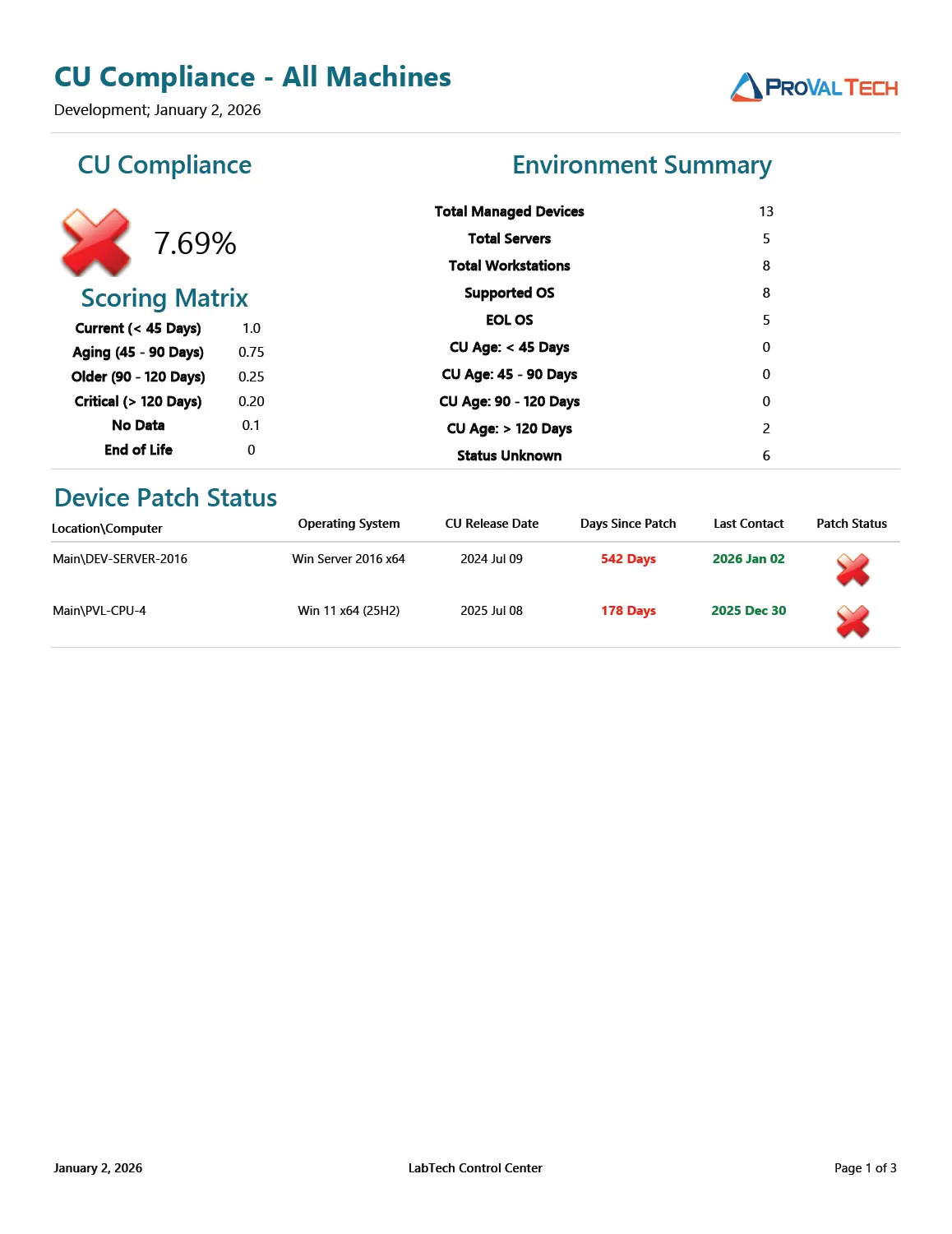
The overall CU Compliance percentage is calculated based on a weighted scoring system. Each machine is assigned a point value between 0 and 1.0 depending on how recently its last Cumulative Update was installed.
Formula: Compliance % = (Sum of all Device Scores / Total Number of Production Machines) * 100
Scoring Matrix:
The report uses the following weights to determine a device's score:
- 1.0 (100%): CU installed within the last 45 days.
- 0.75 (75%): CU installed between 45 - 90 days ago.
- 0.25 (25%): CU installed between 90 - 120 days ago.
- 0.20 (20%): CU installed more than 120 days ago.
- 0.10 (10%): No Data / Unknown. The machine is supported, but Automate has not retrieved CU information.
- 0.00 (0%): End of Life (EOL). The OS version is no longer supported by Microsoft (e.g., Windows 11 22H2).
Example Calculation:
Based on a sample report with 13 Total Devices:
- 0 devices are current (< 45 days) ->
0 * 1.0 = 0 - 0 devices are aging (45-90 days) ->
0 * 0.75 = 0 - 2 devices are critical (> 120 days) ->
2 * 0.20 = 0.40 - 6 devices are status unknown ->
6 * 0.10 = 0.60 - 5 devices are EOL ->
5 * 0.00 = 0
Total Score: 0 + 0 + 0.40 + 0.60 + 0 = 1.0
Calculation: (1.0 / 13) * 100
Final Compliance: 7.69%
Report Sections
1. Environment Summary
This section provides a quick statistical breakdown of the environment. It displays the total count of Managed Devices, Servers, and Workstations. It also groups devices by their patch age category (Current, Aging, Critical) and Support status (Supported vs. EOL).
2. Device Patch Status
This detailed list shows supported machines where the Last Cumulative Update date is known.
- Columns: Includes Computer Name, OS, CU Release Date, and Days Since Patch.
- Purpose: Use this to identify specific machines that are technically "active" but have not successfully applied a monthly update in a long time.
3. No Audit Information
This section lists Supported OS machines (excluding EOL) where the CU information is currently missing or blank.
- Context: These machines result in a score of 0.1.
- Troubleshooting: If this list is populated, it usually means the audit script has not run recently, or the machine has been offline during the scan window.
4. Non-Compliant Devices (EOL)
This section lists all machines running an Operating System version that has reached End of Life.
- Context: These machines automatically receive a score of 0.
- Risk: EOL devices no longer receive public security updates and pose a significant security risk to the network.
Recommendations & Solutions
Based on the data presented in the report sections, the following actions are recommended:
- High count in "No Audit Information": If a large number of devices appear in this section, verify that the Latest Installed Cumulative Update solution is scheduled and running correctly in Automate. This ensures patch dates are retrieved from the endpoint.
- High count of EOL Workstations: If the "Non-Compliant Devices" section contains many Windows 10 or older Windows 11 versions (e.g., 22H2/23H2), you should implement the Windows 11 Latest Feature Update installation solution. This automates the upgrade process to bring these workstations to a supported version (e.g., 24H2).
- Servers in EOL: If servers appear in the "Non-Compliant Devices" list (e.g., Server 2012 R2), immediate planning for an OS migration or server replacement is required, as these cannot simply be "patched" to a compliant state.
Dependencies
- Custom Table - plugin_proval_windows_os_support
- View - plugin_proval_computerpatchcompliance
- View - plugin_proval_clientpatchstats
- View - plugin_proval_clientpatchstatsserver
- View - plugin_proval_clientpatchstatsworkstation
- Script - MySQL - Views for Cumulative Update reports*
- Solution - Latest Installed Cumulative Update
- Solution - CU Compliance Reporting
Sample Report
Click this image to view full report