CWM - Automate - Template - MSI Deployment
This document is crafted to walk you through the utilization of the Template - MSI Deployment for creating a software installation script that employs a .msi file for the installation process.
Steps
-
Export the
Template - MSI Deploymentscript from our environment and import it to the client environment. -
Right-click on the script and select Duplicate.
-
Rename the copied script to something pertaining to what you are installing, as shown below:
-
Right-click the newly renamed software install script and select Send To → Script Folder → Send to the 'ProVal - Client Specific' folder.
-
Delete the template script from the environment to ensure we do not have any issues with the script getting updated and replacing the modifications done.
-
Figure out the complete command to silently deploy the application.
-
Determine the precise application name by inspecting the Software tab on the computer where it is currently installed.
-
Verify the authenticity of the download URL for the application. The download URL may either be the custom link generated to retrieve a file from LTShare or the direct download link for the .msi package.
-
Set the required values in the Dynamic Properties of the script.

ticketcreationcategory: (Step 3): This is used to set an ID for a ticket category, which is necessary to activate the ticketing system for any failures. Setting it to 0 will disable the ticketing feature of the script.DownloadURL: (Step 5): This is the URL from which the .msi package can be downloaded.SoftwareName: (Step 7): This is the exact name of the application as it appears in the software tab of a machine where it has already been installed.AppName: (Step 9): This is the name used to store the .msi package on the endpoint. It’s recommended to avoid spaces or special characters in the package name.AdditionalParameters: (Step 11): These are the extra parameters required to install the script, apart from themsiexec /qn /i \"<Package Path.msi>\". For example, if the complete command to install an application named ABC ismsiexec /qn /i \"C://Temp//ABC.msi\" /noreboot ACCEPTEULA, then/noreboot ACCEPTEULAshould be stored in this variable.
Example
Let’s consider a scenario where one of our partners, referred to as The Partners, has asked us to develop a script for installing an application that utilizes a .msi package for deployment.
The application is known as An Msi Application, a name you discovered from the Software Tab on a computer where it’s already installed.
The Partners have stored the file in their LTShare, specifically in the Transfer/Software directory, and it’s named msipackage.msi.
With this information at hand, we are now equipped to deploy the application. So, it’s time to construct the script.
-
Copy the script titled
Template - MSI Deploymentlocated in theProVal - Templatesfolder. Rename the copied script toDeploy An Msi Application. -
Generate the download URL to download the installer. That would be
https://fqdnofthepartner/labtech/transfer/software/msipackage.msiin this case. Ensure that the download URL can download themsipackage.msifile. -
Figure out the complete installation command for the
msipackage.msipackage. Let's say the command needed to install the application ismsiexec /qn /i \"msipackage.msi\" /noreboot /Allowsomething=1 /AllUsers AcceptEULA. -
Now we have all the values to configure the Global Variables.
-
Set the Dynamic Variables.
TicketCategory: Leave this variable as0, since we do not have any information on whether the partner expects a failure ticket or not.
DownloadURL:https://fqdnofthepartner/labtech/transfer/software/msipackage.msi
SoftwareName:An Msi Application
AppName:msipackage
AdditionalParameters:/noreboot /Allowsomething=1 /AllUsers AcceptEULA
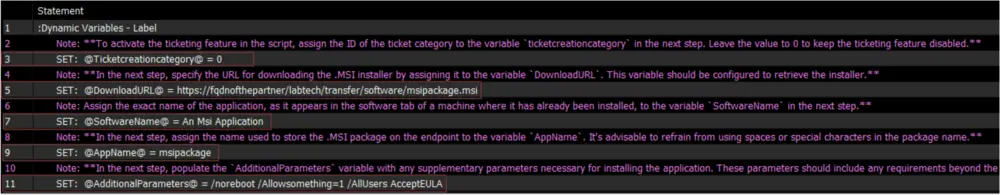
You do not need to convert the symbols. The conversion portrayed in the screenshot is performed by Automate itself. -
Save the script and test it.
-
After the script is prepared, please verify with the partner or consultant whether they would like the script to also generate a ticket in case of failure. If needed, assign the appropriate ticket category ID to the
ticketcreationcategoryvariable.